Introduction to Data Structure
Introduction to Data Structure and Analysis of Algorithm (DSA) Using "C"
Objectives
Ø To understand how
various data structures can be classified into various ways.
Ø To understand the most
commonly used and basic data types and user defined data types.
Ø
To understand the characteristics, functionality and methodology
of problem-oriented data structures used to solve specific problems as well
as how to use a data structure for program implementation.
Why use this Data
Structure OR Need of Data Structure
Ø It gives different
level of organization data model.
Ø It tells how data can
be stored and accessed in its basic level.
Ø Provide operation of
data and data item such as adding an item, deleting an item, getting up
highest priority item.
Ø Provide fast searching
and sorting, accessing of data in data list.
Ø Provide a means to
manage and analysis of huge amount of data efficiently.
Ø It enables attribute
values to be retrieved quickly-assertions are indexed by the entities.
Ø Properties and attributes
of relations are easy to describe.
Ø It allows simple and
powerful of consideration as it embraces aspects of problem oriented with
object oriented programming.
What is Data
Data:
- Data
is raw material of fact and figure of unorganized way that need to be
processed. Data can be something simple, unordered and useless until it is
organized.
What is Information
Information: - When data is processed,
organized, structured or presented in a given context so as to make it useful
for decision making, it is called information.
Data & Information
Data are the
raw materials of facts and figure or details from which information is
derived. Single pieces of data are rarely useful alone. When data to become
information then data needs to be put into context.
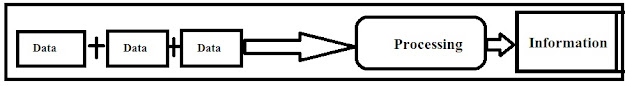
Information = Instruction + Data
Difference Between Data and Information:-
Data
Information
Data is a single unit
Information is a collection of meaningful
data.
Data doesn’t carry a meaning
Information must carry a logical meaning.
Data is the raw material
Information is the product.
Data is used as input for the machine
Information is the output of data in machine.
Data doesn’t depend on Information
Information totally depends on data because we can’t make any
information without data.
Data is not special
Information is special and important.
BASIC
TERMINOLOGY (In Term of Data structure)-ELEMENTARY DATA ORGANIZATION
Data
and Data Item
Data are
simply group or collection of facts and figures. Data are values or group of
values.
A
data item or value refers to a single unit of items
or values. Data items that are divided into sub items are group items; those
that are not are called elementary items.
Example-A
student’s name may be divided into three part- sub items – first name, middle name and last name , address
has three parts –Street, Area and State
but the ID No. of a student would normally be act as a single item.
In
the above example (ID No, Age, Gender, First Name, Middle Name, Last Name,
Street, Area, State) are elementary data values or data items, whereas (Name,
Address ) are group data values or items.
Data Type
Data
type is a tells about the data means which type of data store in particular
variable and identifying one of different types of data such as integer,
floating character and Boolean values that determines the possible values for
that type; and the operations that can be done on values of that type.
It
is the two types of Data Types:-
1. Basic or Primitive Data Type and
2. User defined or Non-Primitive Data Type
1. Primitive data type is the basic data
type that is provided by the programming language with built-in support i.e. int, char float etc. This data type is directly
use by machine to the programming language and is supported by machine
directly while non-primitive data type is derived from primitive data type.
Example- Array, Structure and Union etc.
Variable
Variable is an identifier which hold the data value. It
is a symbolic constant name given to some known data value for the purpose of allowing the name to be used independently of the
data it hold. A variable name in program is usually reference with a data storage location and also its contents and these
may change during the program execution.
Record
A set or group of related data value or data items is known as record. The elements of records are usually
called fields or members. Records are distinguished from arrays list or column by the fact
that their number of fields is typically fixed and each field has a unique name and
that each field may have a different data value.
Entity
An
entity is something about data that has certain attributes which may be
assigned some data items or values. The data values or items themselves may
be either numeric or non-numeric.
Example:
Attributes->
Name
Age
Gender
Values->
Ajay
32
M
Vijay
25
M
Aliza
22
F
Entity Set
An entity set is a group or
collection of similar entities.
Example- Employees of an organization, students of a
class and sports team etc.
Each attribute or properties of an entity set has a
range of values and the set of all possible data values or items that could be
assigned to the particular attributes.
The
term “information” is sometimes used for data with given specified attributes
where meaningful or processed data.
Field
A field is a single unit of data or information identifying
an attribute of an entity a record
is the collection of field items or values of a
given entity and a file is the group of records of the entities in a given
entity set.
File
File is a group of records of the entities in a
given entity set. Example -File containing
records of students of a particular class.
Key
A key means search value is one or more field(s)
in a record that take(s) unique values and can be used to one record from the
others records.
Next Topic-
Our Data Structure and Analysis of Algorithm (DSA) Using C tutorials will guide you to learn DSA one step at a time.
Enroll in our DSA Course for FREE.
|
Objectives |
|
Ø To understand how
various data structures can be classified into various ways. Ø To understand the most
commonly used and basic data types and user defined data types. Ø
To understand the characteristics, functionality and methodology
of problem-oriented data structures used to solve specific problems as well
as how to use a data structure for program implementation. |
|
Why use this Data
Structure OR Need of Data Structure |
|
Ø It gives different
level of organization data model. Ø It tells how data can
be stored and accessed in its basic level. Ø Provide operation of
data and data item such as adding an item, deleting an item, getting up
highest priority item. Ø Provide fast searching
and sorting, accessing of data in data list. Ø Provide a means to
manage and analysis of huge amount of data efficiently. Ø It enables attribute
values to be retrieved quickly-assertions are indexed by the entities. Ø Properties and attributes
of relations are easy to describe. Ø It allows simple and
powerful of consideration as it embraces aspects of problem oriented with
object oriented programming. |
|
What is Data |
|
Data:
- Data
is raw material of fact and figure of unorganized way that need to be
processed. Data can be something simple, unordered and useless until it is
organized. |
|
What is Information |
|
Information: - When data is processed,
organized, structured or presented in a given context so as to make it useful
for decision making, it is called information. |
|
Data & Information |
|
Data are the
raw materials of facts and figure or details from which information is
derived. Single pieces of data are rarely useful alone. When data to become
information then data needs to be put into context.
|
Information = Instruction + Data
Difference Between Data and Information:-
|
Data |
Information |
|
Data is a single unit |
Information is a collection of meaningful
data. |
|
Data doesn’t carry a meaning |
Information must carry a logical meaning. |
|
Data is the raw material |
Information is the product. |
|
Data is used as input for the machine |
Information is the output of data in machine. |
|
Data doesn’t depend on Information |
Information totally depends on data because we can’t make any
information without data. |
|
Data is not special |
Information is special and important. |
|
BASIC
TERMINOLOGY (In Term of Data structure)-ELEMENTARY DATA ORGANIZATION |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Data
and Data Item |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Data are
simply group or collection of facts and figures. Data are values or group of
values. A
data item or value refers to a single unit of items
or values. Data items that are divided into sub items are group items; those
that are not are called elementary items. Example-A student’s name may be divided into three part- sub items – first name, middle name and last name , address has three parts –Street, Area and State but the ID No. of a student would normally be act as a single item. In
the above example (ID No, Age, Gender, First Name, Middle Name, Last Name,
Street, Area, State) are elementary data values or data items, whereas (Name,
Address ) are group data values or items.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Data Type |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Data
type is a tells about the data means which type of data store in particular
variable and identifying one of different types of data such as integer,
floating character and Boolean values that determines the possible values for
that type; and the operations that can be done on values of that type.
It
is the two types of Data Types:- 1. Basic or Primitive Data Type and 2. User defined or Non-Primitive Data Type
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Variable |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Variable is an identifier which hold the data value. It
is a symbolic constant name given to some known data value for the purpose of allowing the name to be used independently of the
data it hold. A variable name in program is usually reference with a data storage location and also its contents and these
may change during the program execution.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Record |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
A set or group of related data value or data items is known as record. The elements of records are usually
called fields or members. Records are distinguished from arrays list or column by the fact
that their number of fields is typically fixed and each field has a unique name and
that each field may have a different data value. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Entity |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
An
entity is something about data that has certain attributes which may be
assigned some data items or values. The data values or items themselves may
be either numeric or non-numeric. Example:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Entity Set |
||||||||||||||||||||
| An entity set is a group or
collection of similar entities. Example- Employees of an organization, students of a class and sports team etc. Each attribute or properties of an entity set has a range of values and the set of all possible data values or items that could be assigned to the particular attributes.
|
Next Topic-
Enroll in our DSA Course for FREE.


Comments
Post a Comment